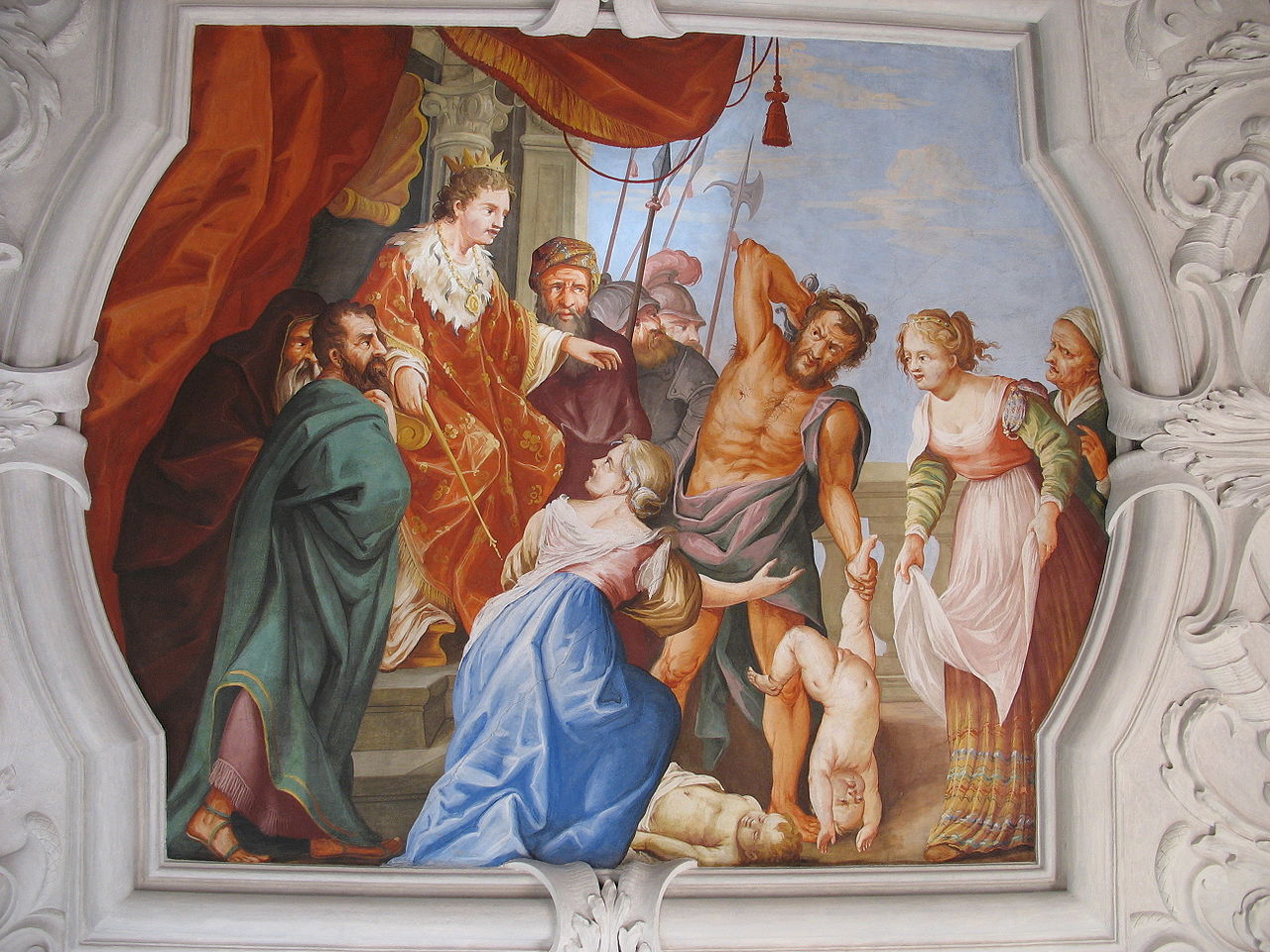
His famous judgment, named after him, has also been handed down: In a dispute between two mothers over a child, Solomon ordered them to divide the child so that each had one half. The false mother agreed, betraying her deceit. A true mother would never allow such a thing.
At that time, two harlots came and stood before the king. One said, "Please, sir, I and this woman live in the same house, and I gave birth there in her presence. On the third day after I gave birth, this woman also gave birth. We were together. No stranger was in the house with us, only the two of us were there. Now this woman's son died during the night; for she had smothered him in his sleep. She got up in the middle of the night, took my child from me while your maid slept, and laid him by her side. But her dead child she laid by my side. When I got up in the morning to nurse my child, it was dead. But when I looked closely at it in the morning, it was not my child that I had borne."
Then the other woman cried out, "No, my child is alive, and your child is dead." But the first replied, "No, your child is dead, and my child is alive." The child was brought before the king, and the women continued their quarrel. Then the king began, "This one says, 'My child is alive, and your child is dead!' and that one says, 'No, your child is dead, and my child is alive.'" And the king continued, "Get me a sword!" Now he decided, "Cut the living child in two, and give half to one and half to the other!"
But now the mother of the living child begged the king - for maternal love for her child stirred in her: "Please, Lord, give her the living child, and do not kill it!" But the other cried, "It shall not be mine nor yours. Cut it up!" Then the king commanded, "Give the living child to that one, and do not kill it; for she is its mother."
With this judgment Solomon became legendary and all looked up to him with awe. They recognized him as the wisdom of God when he spoke justice.









Comments
Links