Charles Darwin was born on 12 February 1809 in Shrewsbury, near Birmingham, the fifth of six children of Robert Darwin, a doctor, and his wife Susannah, née Wedgwood. When Charles was eight years old, his mother died of a gastrointestinal illness, so he was brought up by his three older sisters Marianne, Caroline and Susan.
Charles Darwin (1809 to 1882)
BackThe inventor of the theory of evolution
He was born into a rich family and was able to devote himself entirely to his research due to his financial independence. He developed the well-known theory of evolution, which is still understood as fact in principle, even if not in detail.
- 1809: Charles Darwin is born on 12 February in Shrewsbury, England
- 1817: Darwin's mother dies in Shrewsbury (England)
- 1818 - 1825: Attends private boarding school in Shrewsbury
- 1825 - 1827: Studies medicine, but without a degree
- 1828 - 1831: Studies in theology at Cambridge
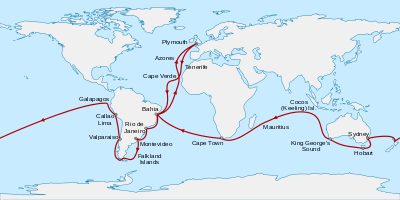
- 1831 - 1836: Voyage on the H. M. S. Beagle
- 1836: Darwin falls ill with an unknown disease. The symptoms accompany Darwin throughout his life
- 1837: First draft of the theory of evolution. More than 20 years pass before publication
- 1839: Darwin marries his cousin Emma Wedgwood. Ten children are born of this marriage
- 1853: Darwin is awarded the Royal Medal
- 1859: Publication of "On the Origin of Species"
- 1864: Darwin is awarded the prestigious Copley Medal for his research
- 1871: Publication of "The Descent of Man and Sexual Selection"
- 1882: Charles Darwin dies on 19 April in Downe (London)
Education at various schools (1818)
He first attended a day school run by the Unitarian congregation, and in 1818 he transferred to a private boarding school in Shrewsbury, where he remained until 1825. Even as a schoolboy he was interested in nature and made his first chemical experiments with his older brother Erasmus.
From 1825, Darwin studied medicine in Edinburgh. At his father's insistence, he had to switch to theology. However, he also attended lectures in natural sciences such as geology and botany at Cambridge.
Marriage and founding of a family (1839)
On 29 January 1839, Charles Darwin married his cousin Emma Wedgwood. He was fortunate to have a fortune through his ancestors' money and was able to live a financially independent life. He had ten children:
- William Erasmus (1839)
- Anne (1841)
- Mary Eleanor (1842)
- Henrietta (1843)
- George Howard (1845)
- Elizabeth (1847)
- Francis (1848)
- Leonard (1850)
- Horace (1851)
- Charles Waring (1856)
The Darwins' beloved eldest daughter, Annie, fell ill and died shortly after she turned ten. Darwin was so overcome with grief that he could not go to her funeral. The daughter's death was also a strain on the marriage. He decided not to go to the church anymore.
Charles Darwin undertook a great voyage of discove (1831)
The circumnavigation of the world on the Beagle, 1831-1836
In 1831, he completed his studies and began a five-year voyage around the world on the survey ship "Beagle".
It took him to South America, the Galapagos Islands, Tahiti, New Zealand, Australia, Mauritius and South Africa. It was during this venture that Darwin decided on natural history research as his career.
On the ship he read the writings of Sir Charles Lyell and was influenced by his theories and developed his own ideas on the evolution of life. On the Galapagos Islands, Darwin observed various species of finches, which later led him to develop the theory of selection.
He was also influenced by the English economist Thomas Robert Malthus. According to his theories, the natural and social regulation of human overpopulation was governed by hunger, disease, wars and natural disasters. Darwin applied these mechanisms to the animal and plant world. In the process, he came to the realisation that living organisms are subject to evolution.
After this great journey of research, Darwin began to experience increasing symptoms of illness from which he never fully recovered. He therefore withdrew more and more and never left Great Britain again for the rest of his life.
Move to Downe (1842)
In 1842 the family moved to Downe, in the county of Kent, south of London, which Darwin hoped would improve his symptoms. There he lived with his family in a former vicarage called "Down House" and also wrote his two main works. In addition to his scientific abilities, Darwin was also considered an excellent draughtsman.
His other works include titles such as "The Variation of Animals and Plants Under Domestication (1868)", "The Descent of Man" (1871) and "The Expression of the Emotions in Animals and Man" (1872).
Development of the theory of evolution (1859)
Influenced by the discoveries on his world tour, he developed his theory of evolution by 1859 and published his main work, On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection. The book was a great success and appeared in several editions. The core statement was that the more highly developed creatures descended from the less highly developed ones and thus implied his theory of evolution. Darwin's theory of selection is based on the assumption that from a surplus of offspring, only those creatures survive that are best able to adapt to living and environmental conditions. In the constant struggle for food and living space, the hereditary material is thus passed on which is most advantageous. He assumed that evolution also had to produce new species.
In this process, Darwin also took into account the fact of chance. Darwin's theory of evolution was opposed to the common catastrophe theory of George Cuvier. This theory stated that existing living beings fell victim to natural disasters. Subsequent living beings had not evolved from the previous ones, but represented new species. One such catastrophe was the Flood, which wiped out everything except the creatures in Noah's Ark. The living humans and animals are therefore direct descendants of that time.
Deepening the theory of evolution (1871)
In his second major work, The Descent of Man and Sexual Selection, Darwin partially applied his theory of evolution to humans. This brought him into conflict with the Church, which regarded mankind as the crown of creation.
Charles Darwin became a member of the Royal Society in 1839 and a member of the French Academy of Sciences in 1878. His theory of descent made Charles Darwin one of the most important natural scientists.
His other works include titles such as "The Variation of Animals and Plants Under Domestication (1868)", "The Descent of Man" (1871) and "The Expression of the Emotions in Animals and Man" (1872).
In the timeline of humanity he is remembered as the father of the evolution theory.
Embedded Videos
EVOLUTION AND CHARLES DARWIN - NOVA - Discovery History Science (documentary)
Charles Darwin Documentary Biography HD
The Making of a Theory: Darwin, Wallace, and Natural Selection
Darwin and the Theory of Evolution Documentary
Charles Darwin directly against religion
Comments & Conclusions
Where Darwinism can lead
Social Darwinism can also be derived from Darwin's theory of evolution. This means that the stronger survives and the weaker disappears. Behind this is an inhuman view of marginalised groups in society and the socially weaker. But not only on individuals, but also on whole peoples. This is about the "struggle for existence" and the "survival of the fittest".
Historical Social Darwinism experienced its zenith in the second half of the 19th century and at the beginning of the 20th century. At that time, there were Social Darwinists in all political camps, from socialists to liberals to National Socialists. Each group took from Darwinian theory what it could use for its goals. This rationale was used, for example, to unleash a Nazi extermination campaign in the East during the Second World War.
The theory of evolution completely contradicts the Bible's teaching on creation. It is more than just a question of how old the world is and how everything came into being. It is about the question of whether there is a creative force behind life or whether everything came into being by chance.
Simultaneous events, periods or persons of Charles Darwin
| Persons/Events/Periods | Subcategory | From | To | Reason of importance |
|---|










Comments
Links